4 min read
Incident Management Strategies in Value Based Care
Performance Health Partners
February 12, 2024
Healthcare’s move toward value-based care (VBC) represents a paradigm shift, emphasizing the quality and outcomes of care rather than the volume of services provided. This approach necessitates a robust incident management system to ensure patient safety and high-quality healthcare delivery. This blog post explores various incident management strategies crucial to the implementation and success of a value-based care model, examining their significance, methodologies, challenges, and solutions.
Understanding the Value-Based Care Model
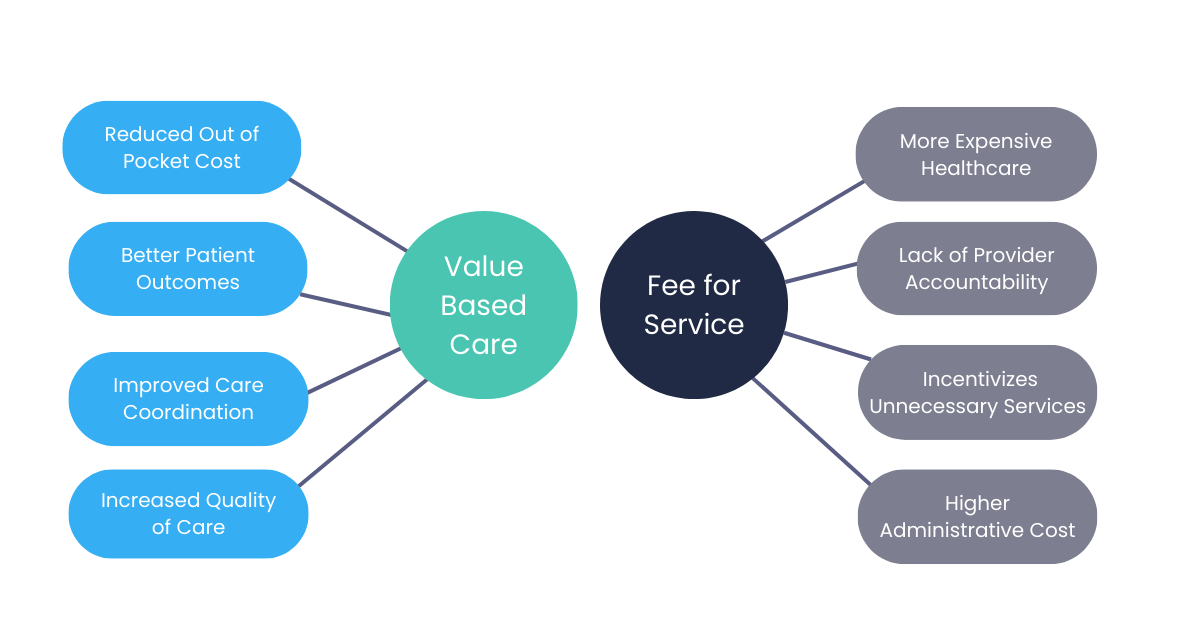
Value-based care is a transformative healthcare delivery model emphasizing the quality of care over the quantity of care. With value-based care, healthcare providers are incentivized to offer care that’s not only effective but also cost-efficient. This model stands in stark contrast to the traditional fee-for-service system, where the focus is on the quantity of care, often leading to unnecessary procedures without necessarily improving patient outcomes.
In VBC, providers are compensated based on patient health outcomes, incentivizing them to deliver higher quality care at lower costs.
Value-based care models are increasingly common, accounting for about 40% of payments between 2016 and 2023. It’s estimated that 238.8 million Americans receive health care in a value-based care model.
The Critical Role of Incident Management in VBC
In the value-based care framework, incident management plays a crucial role. It involves identifying, analyzing, and responding to incidents to prevent or minimize harm to patients. Effective incident management in VBC isn’t just reactionary but also proactive, focusing on preemptive measures to avoid incidents and other patient safety events.
This proactive approach is essential, as it directly impacts the two pillars of VBC: patient outcomes and care quality.
Proactive Risk Assessment: A Key Strategy
One of the foremost strategies in incident management within the context of value-based care is proactive risk assessment. This preventative approach involves identifying potential risks before they manifest into incidents.
For instance, leveraging data analytics to predict which patients are at higher risk of adverse drug reactions can prevent medication errors. This strategy aligns perfectly with the objectives of VBC, where the focus is on preventing incidents to improve overall patient health outcomes.
Leveraging Data for Predictive Analysis
Utilizing data effectively for predictive analysis is a critical component of proactive risk assessment. Healthcare organizations can employ advanced data analytics tools to analyze patient data and identify potential risk factors.
This can range from analyzing past incident reports to using sophisticated algorithms that predict possible future events based on current patient data. Such predictive capabilities allow healthcare providers to implement targeted interventions that can prevent potential incidents, thereby improving patient safety and care quality.
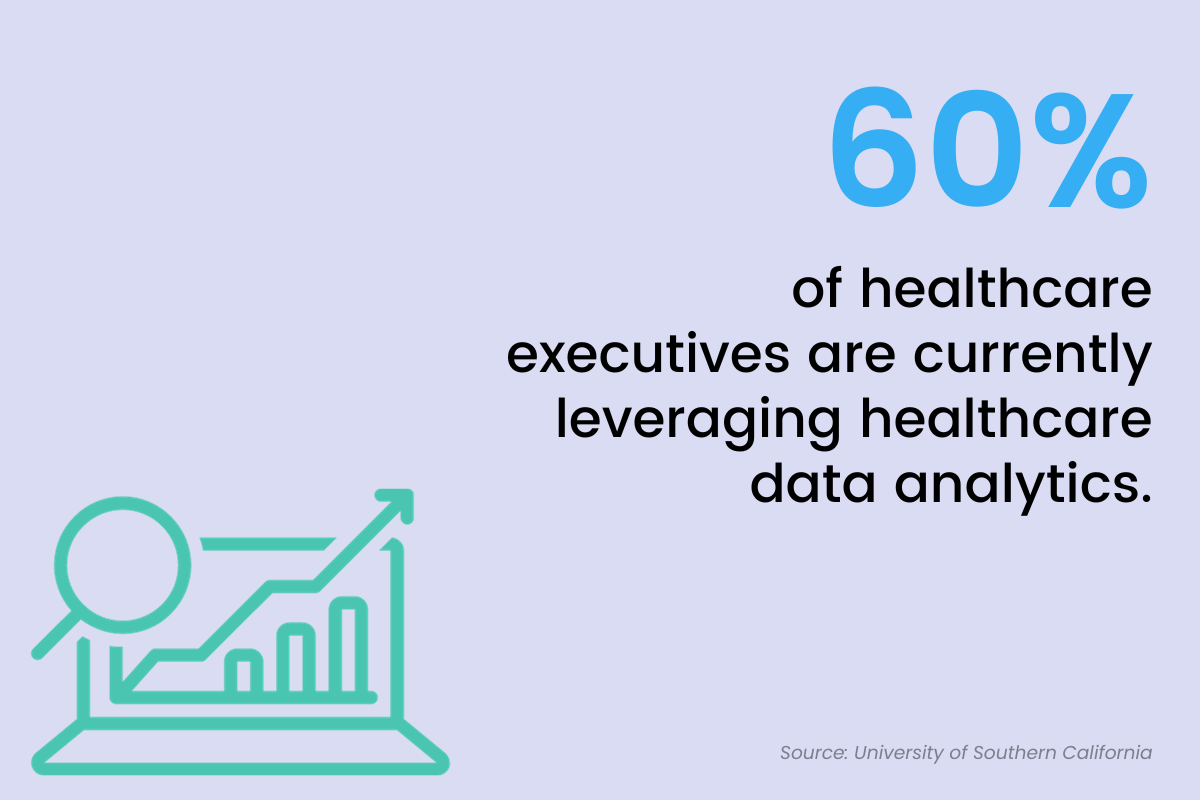
The momentum for data analytics in the healthcare sector is on the rise.
A recent survey by the Society of Actuaries indicates that 60% of healthcare executives are currently leveraging healthcare data analytics in their organizations. Among these executives, 42% observed improved patient satisfaction, and 39% reported cost savings.
The adoption of data analytics in healthcare is further fueled by value-based programs initiated by the U.S. Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services. Notably, the Hospital Value-Based Purchasing (VBP) Program provides financial incentives to hospitals that demonstrate improved performance in healthcare delivery.
Transparent Incident Reporting & Analysis
An open and transparent incident reporting system is a cornerstone of effective incident management in value-based care. That’s why it’s crucial to foster an environment where healthcare professionals feel safe to report incidents. This transparency is key to gaining a comprehensive understanding of the nature and causes of adverse events.
Importance of a Non-Punitive Culture
Establishing a non-punitive culture is essential for encouraging incident reporting. Healthcare providers should be assured that the focus of incident reporting is on learning and improving, rather than assigning blame. This approach can lead to a more open reporting environment, where staff members are more likely to report near misses and adverse events, providing valuable data for improving patient care practices.
Cultivating a culture of safety fosters open communication and trust. However, there may be specific scenarios in which healthcare workers might still be reluctant to report incidents due to various factors. In these cases, anonymous reporting should be encouraged.
Research shows that 74% of employees express a greater willingness to provide feedback when it is truly anonymous.
Data-Driven Decision Making
The data collected from incident reports should be meticulously analyzed to identify trends and patterns in patient safety processes. This analysis can inform changes in clinical practices, protocols, and policies. Data-driven decision making ensures that improvements to healthcare delivery are evidence-based, enhancing the effectiveness of patient care under the value-based care model.
Implementing Continuous Improvement
Continuous improvement is a fundamental principle in effective incident management strategies, especially in the realm of value-based care. Learning from every incident, whether it results in harm or not, provides invaluable insights for enhancing healthcare delivery.
Employees not only become better informed but are also more inclined to stay with the company when the company implements continuous improvement and learning from every incident.
Learning and Adapting from Incidents
Each reported incident offers an opportunity for learning and improvement. Healthcare organizations should analyze these incidents to understand their root causes and implement measures to prevent recurrence. This may involve updating clinical protocols, revising training programs, or even overhauling certain aspects of healthcare delivery.
Quality Improvement Initiatives
Quality improvement initiatives are vital in implementing changes based on insights gained from incident reports. These initiatives may include staff training programs, process re-engineering, or adopting new technologies. The goal is to continuously enhance the quality of care in alignment with the principles of value-based care.
For example, hospitals often face challenges related to hospital-acquired conditions experiencing by patients. In response to incident reports and insights gained from analyzing events such as infections acquired during a patient’s hospital stay, a healthcare facility might initiate a training program for healthcare staff focusing on proper hygiene protocols, infection control measures, and the appropriate use of personal protective equipment to improve the quality of care.
Overcoming Implementation Challenges
While the benefits of effective incident management in value-based care are clear, implementing these strategies can be challenging.
One of the significant barriers to effective incident management is cultural resistance within healthcare organizations. There might be a reluctance to change existing practices or a fear of repercussions from reporting incidents. Addressing this requires leadership commitment to fostering a culture of safety and learning. Leaders should advocate for open communication, encourage reporting, and ensure that the focus is on improvement rather than punishment.
Another challenge is the technological and resource constraints that many healthcare organizations face. Implementing an effective incident management system often requires substantial investment in technology and training. Overcoming these constraints might involve seeking additional funding, prioritizing resource allocation, or exploring innovative, cost-effective solutions.
In the evolving landscape of value-based care, incident management plays a pivotal role in ensuring high-quality, patient-centered care. By focusing on proactive risk assessment, transparent reporting and analysis, cultivating a culture of safety and continuous improvement, and overcoming implementation challenges, healthcare providers can effectively manage incidents.
This approach not only aligns with the principles of value-based care but also represents a commitment to delivering the highest standards of healthcare. As the healthcare industry continues to evolve, the strategies and principles discussed here will remain fundamental in ensuring that patient safety and care quality are at the forefront of healthcare delivery.



