4 min read
What is Value Based Care? A New Era of Healthcare
Performance Health Partners
October 8, 2019
The models of care used by healthcare organizations have evolved over time. One of the most significant healthcare paradigm shifts in the past decade is the introduction of a new reimbursement model known as value based care. But what is value based care?
A New Era of Healthcare
Where the traditional fee-for-service model rewarded organizations that treated the highest number of patients, the value-based care model now rewards organizations that provide the highest-quality care (1).
This transition has driven organizations to achieve higher levels of patient safety and quality monitoring so that they can maximize reimbursement and maintain fiscal stability.
The Movement Towards Value Based Care Model
The Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services defines value-based care as
“programs that reward healthcare providers with incentive payments for the quality of care they give to patients” (2).
The goal of value-based care is to make healthcare proactive instead of reactive, so that potential problems are prevented before they start (1).
With this goal in mind, a new of value in healthcare called “the value equation” has emerged:

where the value of the service is directly related to the quality of care and outcomes achieved, as opposed to the quantity of provider visits (3).
The Expansion of Value-Based Care
Value-based care programs are rapidly expanding across the U.S., with a seven-fold increase in the number of states implementing such initiatives in the past five years (4). According to a recent study by Change Healthcare, Value-Based Care in America: State-by-State, as of April 2019 (4):
- 48 states have implemented value-based care or payment programs
- 50% of those programs are multi-payer in scope, and
- just four states have little or no value-based care initiatives underway.
Today, nearly two-thirds of payment are based on value (5).
Benefits of Value Based Care
There are several areas of opportunity emerging for healthcare organizations due to the movement towards value-based care: the opportunity to improve patient outcomes, actively engage patients and staff, reduce costs, and increase reimbursement.
1. Improve Patient Outcomes
Patient outcomes are the cornerstone of high-quality, value-based care. Accordingly, a robust tool for tracking patient data and analytics is of critical importance in optimizing resources and improving outcomes.
On average, patient charts cannot be found on 30% of visits, and 3 out of every 10 tests are reordered because the results cannot be found, which costs organizations time and money (6).
By inputting all patient health information into a secure database, the possibility for patient and safety data to be physically lost or misplaced is drastically reduced, which improves the quality of patient outcomes and maximizes value of care.
2. Reduce Costs
According to the AHRQ National Scorecard on Hospital-Acquired Conditions, national efforts to reduce hospital-acquired conditions such as adverse drug events and injuries from falls helped prevent 20,500 deaths and saved $7.7 billion between 2014-2017 (7).
These reductions in harm are directly related to value-based care and improving the quality of patient's experiences. Risk is reduced by spreading it across a larger patient population. Value-based payment also allows payers to increase efficiency by bundling payments that cover the patient’s full care cycle, or for chronic conditions, covering periods of a year or more (8).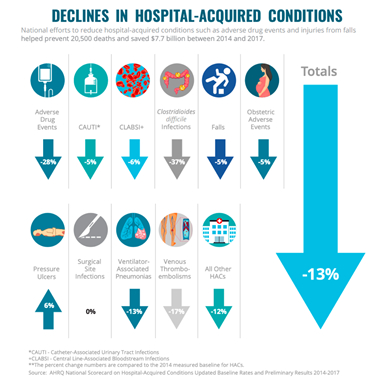
3. Increase Reimbursements
Healthcare organizations have the opportunity to drastically increase their reimbursements through value-based care. While providers might spend more time on new, prevention-based services, they will spend less time on chronic disease management. By focusing on quality instead of quantity, providers have the opportunity to increase their quality and patient engagement measures, thereby maximizing their reimbursements (7).
4. Actively Engage Patients
Focusing on the value of care leads to actively engaged patients and staff. One way that healthcare organizations can achieve this goal is to implement a patient relations survey tool, where patients can easily give feedback on the care provided.
 As it relates to the value equation above, when patients are actively engaged in their care, we see an increase in both quality and service, which heightens the value of the service provided and helps organizations maximize their reimbursement.
As it relates to the value equation above, when patients are actively engaged in their care, we see an increase in both quality and service, which heightens the value of the service provided and helps organizations maximize their reimbursement.
5. Actively Engage Staff
Active staff engagement in value-based care has also become a major strategy for increasing value by combating employee burnout and turnover. Craig Deao, a consultant for Huron and a faculty member for the American College of Healthcare Executives, estimated that the average cost of employee turnover in healthcare is almost $27 million/ year (8).
Fortunately, employee engagement in healthcare has emerged as a key tool for improving those rates. As the Healthcare Finance News describes, “a focus on employees’ commitment and emotional investment in their work is a ‘must-have’ core competency for leaders in healthcare” (9), helping to increase engagement across departments.
Many organizations have found that implementing a technology tool for employee engagement can drastically increase employee engagement, which increases the value of the service provided.
What is the Future of Value Based Healthcare?
All of the areas of opportunity outlined above can be achieved through the implementation of data-driven technology solutions.
Although the healthcare industry has seen great success in implementing Electronic Health Record (EHR) systems over the past decade, truly effective solutions go beyond EHR systems to encompass the entire system as a whole. A comprehensive, customizable technology solution can help healthcare organizations maximize their outcomes in value-based care.
What is value based care? Interested in learning more about how a technology solution can help improve patient outcomes? Download our free guide below to learn how to increase quality of care through efficient reporting.
References
- https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/articles/15938-value-based-care
- https://www.cms.gov/Medicare/Quality-Initiatives-Patient-Assessment-Instruments/Value-Based-Programs/Value-Based-Programs.html
- https://www.elationhealth.com/healthcare-innovation-policy-news-blog/history-value/
- https://archive.thepcc.org/sites/default/files/resources/%7Ba7b8bcb8-0b4c-4c46-b453-2fc58cefb9ba%7D_Change_Healthcare_Value-Based_Care_in_America_State-by-State_Report.pdf
- https://hitconsultant.net/2018/06/18/value-based-care-trends/#.XYqOUJNKhQJ
- http://www.techceocouncil.org/clientuploads/reports/A_Healthy_System_Final.pdf
- https://www.ahrq.gov/data/infographics/hac-rates_2019.html https://revcycleintelligence.com/features/what-is-value-based-care-what-it-means-for-providers
- https://catalyst.nejm.org/what-is-value-based-healthcare/
- https://www.healthcarefinancenews.com/news/cure-healthcares-high-employee-turnover-engagement-expert-says


