6 min read
What is Incident Management?: How to Prevent Harm in Healthcare
Performance Health Partners
April 13, 2023
In the healthcare industry, incident management is the backbone of ensuring patient safety and reducing harm in the care setting. Read on for a closer look at what incident management is in healthcare, including the crucial steps involved in the incident management process.
What is Incident Management?
Incident management is a comprehensive process that healthcare organizations use to identify, manage, and resolve incidents that could potentially harm patients or healthcare workers. In other words, incident management is a proactive approach that aims to prevent incidents from occurring in the first place, but also a reactive approach to minimize the impact of any incidents that do occur. The goal of incident management is to provide high-quality patient care and to continuously improve the safety and well-being of patients.
In the healthcare industry, an incident refers to any event that disrupts or has the potential to disrupt the normal delivery of patient care. It could be an unintended event, an error, or a near miss that could lead to harm to a patient or healthcare worker. It is estimated that out of 421 million hospitalizations globally per year, 42.7 million adverse events occur in patients during their hospitalizations.
Examples of incidents in healthcare include but are not limited to:
- Medication errors, such as administering the wrong medication or dose
- Patient falls
- Patient elopement, where a patient leaves the healthcare facility without permission
- Surgical errors, such as performing the wrong procedure or operating on the wrong body part
- Medical device malfunctions
- Patient misidentification, such as administering treatment or medication to the wrong patient
- Infections acquired within the healthcare facility
- Adverse reactions to medications or treatments
- Delay in diagnosis or treatment
- Equipment failures or malfunctions
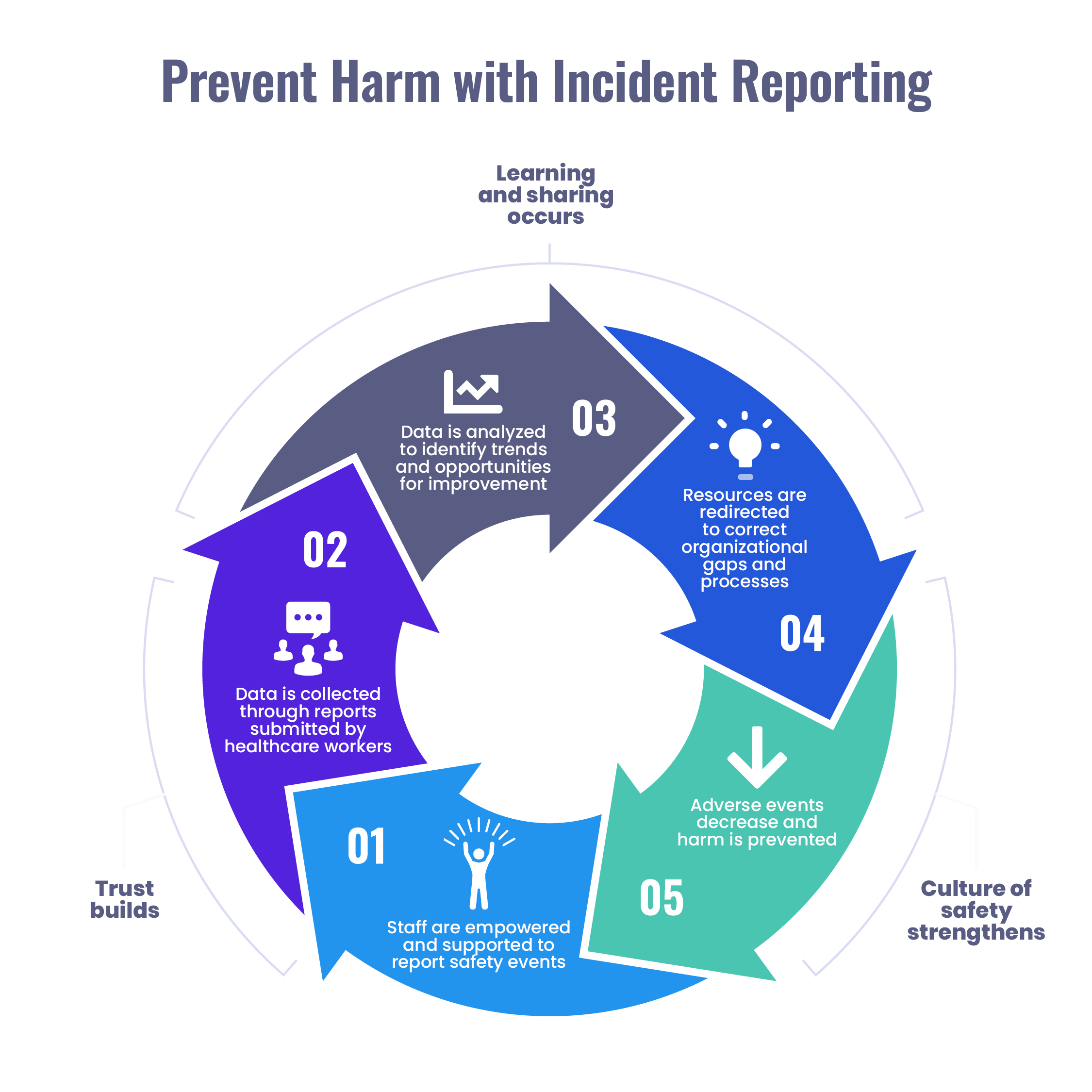
It's essential to report incidents to the appropriate personnel and document them in an incident reporting process. This information can be used to identify trends, implement corrective actions, and prevent incidents from recurring. By having an effective incident management system in place, organizations can utilize valuable insights that can be used to continuously improve patient safety and the quality of care.
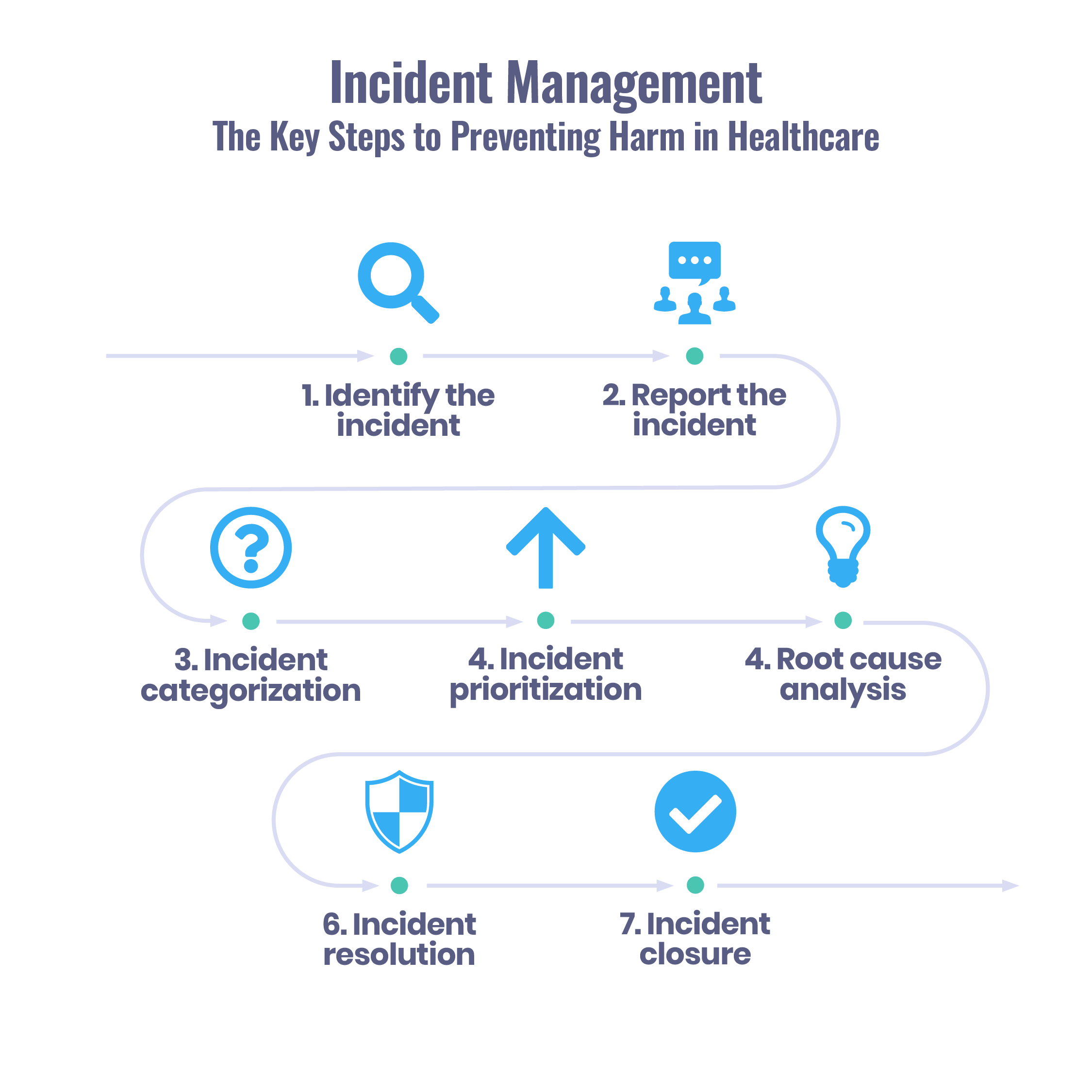
The Steps of the Incident Management Process
The primary goal of incident management in healthcare is to minimize the negative impact of incidents on patient safety and to restore normal patient care as quickly as possible. Incident management involves a set of procedures and tools that help to identify, diagnose, and resolve incidents. The incident management process in healthcare typically consists of the following steps:
Incident Identification
The first step is to identify the incident and gather as much information about it as possible. This can be done through various means, such as patient complaints, incident reporting systems, or electronic medical records. Any healthcare worker who witnesses an incident or near miss should report it to their supervisor or to the incident reporting system.
Once an incident has been identified, it's crucial to gather as much information about it as possible. This includes details such as the date and time of the incident, the location, the people involved, and any contributing factors. There are several ways incidents can be identified in healthcare:
- Patient complaints: Patients or their families may report incidents, such as a medication error or a fall, to healthcare staff. It's crucial to listen carefully to these complaints and take them seriously, as they can provide valuable insights into potential incidents.
- Incident reporting systems: Healthcare organizations often have incident management software in place that allow staff to report incidents or near misses. These systems provide a mechanism for incident documentation and enable healthcare organizations to collect data and analyze trends.
- Electronic medical records: Electronic medical records can provide important information about incidents, such as medication errors or diagnostic delays. Analyzing this data can help identify areas for improvement in patient care.
Incident Logging
After an incident has been identified and the necessary information has been gathered, the next step in incident management is to log the incident in an incident management system. Incident logging is critical for incident management because it allows incidents to be tracked and managed throughout their lifecycle. However, it is important to encourage staff to report errors since less than 10% of medical errors are actually reported.
An incident management system is a software application that enables incident management teams to record and manage incidents. These systems provide a central repository for incident data and allow incident management teams to access and analyze this data to identify patterns and trends.
Incident Categorization
After an incident has been identified and logged in an incident management system, the next step is to categorize the incident. Incident categorization is an essential part of incident management in healthcare because it helps to prioritize incidents and determine the appropriate response time.
Incidents are typically categorized based on their impact on patient safety and urgency. The following are some of the categories used in incident management in healthcare:
- Severity: Incidents are categorized based on their severity, with categories ranging from minor incidents that have little or no impact on patient safety to major incidents that result in serious harm or death. This helps to prioritize incidents and determine the appropriate level of response.
- Urgency: Incidents are also categorized based on their urgency, with categories ranging from low urgency incidents that can be addressed over a longer period of time to high urgency incidents that require an immediate response. This helps to ensure that incidents are addressed in a timely manner.
- Type: Incidents can also be categorized based on their type, such as medication errors, falls, or surgical complications. This helps to identify patterns and trends in incident data and develop targeted strategies to prevent similar incidents from happening in the future. The most common type of error was medication lists, having 29% prevalence.
Incident Prioritization
During this step, the incident is assigned a priority based on its impact and urgency. This determines the response time and the resources that will be allocated to resolve the incident.
The following factors are typically considered when assigning a priority level to an incident:
- Impact on patient safety: The incident's impact on patient safety is a critical factor in determining the priority level. Incidents that pose an immediate threat to patient safety will be assigned a higher priority level than those with a lower impact.
- Urgency: The urgency of the incident is another important factor to consider. High urgency incidents that require immediate attention will be assigned a higher priority level than low urgency incidents that can be addressed over a longer period of time.
- Potential for recurrence: The potential for the incident to recur is also considered when assigning a priority level. Incidents with a higher potential for recurrence will be assigned a higher priority level to ensure that the underlying causes are addressed and similar incidents are prevented in the future.
Root Cause Analysis (RCA)
The next step in incident management in healthcare is to determine the root cause of the event. Root cause analysis involves analyzing the available data to determine the underlying cause of the incident.
The following steps are typically involved in incident diagnosis:
- Gathering information: The incident management team gathers all available information related to the incident, including patient records, incident reports, witness statements, and any other relevant data.
- Conducting an investigation: The team then conducts a thorough investigation to identify the underlying causes of the incident. This may involve interviewing staff members, reviewing policies and procedures, and examining equipment or technology involved in the incident.
- Analyzing the data: Once the investigation is complete, the team analyzes the data to determine the root cause of the incident. This may involve identifying system failures, communication breakdowns, or other factors that contributed to the incident.
- Developing a corrective action plan: Based on the analysis, the team develops a corrective action plan to address the root cause of the incident and prevent similar incidents from occurring in the future. This may involve implementing new policies and procedures, providing additional training to staff members, or modifying equipment or technology.
By diagnosing incidents and identifying their root causes, healthcare organizations can develop targeted strategies to prevent similar incidents from occurring in the future. This can improve patient safety and quality of care, and help to build a culture of safety within the organization.
Incident Resolution
Incident resolution involves taking appropriate actions to resolve the incident and prevent similar incidents from occurring in the future. The following steps are typically involved in incident resolution:
- Implementing corrective actions: Based on the root cause analysis, the incident management team develops a corrective action plan to address the underlying causes of the incident. This may involve implementing new policies and procedures, providing additional training to staff members, or modifying equipment or technology.
- Providing medical treatment: If the incident involves patient harm, the healthcare team provides appropriate medical treatment to the patient. This may involve administering medication, performing procedures, or transferring the patient to another facility for specialized care.
- Modifying patient care plans: If the incident involves a breakdown in communication or other issues related to patient care plans, the healthcare team modifies the plans to ensure that the patient receives the appropriate care.
- Monitoring the incident: After the incident has been resolved, the incident management team continues to monitor the situation to ensure that the corrective actions are effective and that there are no further incidents.
Incident Closure
Once the incident has been resolved and all necessary actions have been taken, it is important to ensure that it is properly closed out in the incident management system.
Incident closure involves several key activities, including:
- Documenting the resolution: The incident management team documents the resolution of the incident, including the actions that were taken to address the root cause and prevent similar incidents from occurring in the future. This documentation serves as a record of the incident and can be used for future reference.
- Communicating with stakeholders: The incident management team communicates with relevant stakeholders, including patients and their families, healthcare providers, and regulatory agencies, to inform them of the incident and its resolution. This helps to ensure transparency and maintain trust in the healthcare organization.
- Conducting a post-incident review: After the incident has been closed out, the incident management team conducts a post-incident review to evaluate the effectiveness of the incident management process and identify areas for improvement. This helps to ensure that the organization is continuously learning and improving its incident management capabilities.
By properly closing out incidents in the incident management system, healthcare organizations can ensure that incidents are fully documented and can be used for future reference. This can help to improve incident management processes over time and ultimately improve patient safety and quality of care.
Leveraging Technology to Improve the Incident Management Process
Incident management software can greatly facilitate and improve the reporting process by providing a centralized platform for incident reporting, tracking, and management. With incident management software, healthcare organizations can streamline the reporting process, improve the accuracy of incident data, and reduce the time and effort required to manage incidents.
Performance Health Partners' incident management system provides a comprehensive and user-friendly platform for healthcare organizations to manage incidents and improve patient safety. Our system allows for easy incident reporting and tracking, with customizable workflows and automated notifications to ensure timely and effective incident resolution.
By using our incident management system, recently named the #1 healthcare safety software in the world, healthcare organizations can reduce the risk of incidents and improve the quality of care provided to patients. Request a demo today to see how Performance Health Partners can help improve your incident management processes.


