3 min read
9 Tips for Performing an Effective Root Cause Analysis in Healthcare
Performance Health Partners
November 14, 2024
Root cause analysis in healthcare is a systematic approach to identifying the underlying causes of problems, medical errors, or adverse events. This strategy is widely utilized to understand what happened, why it happened, and how to prevent it from happening again. As a crucial tool for quality improvement in healthcare, it helps to address gaps in safety processes and improve outcomes.
Here are nine tips to help healthcare professionals conduct an effective root cause analysis (RCA):
1: Foster a Just Culture for Incident Reporting
Encourage a workplace environment where employees feel comfortable reporting errors and near-misses. A just culture promotes transparency and learning from mistakes, rather than assigning blame to an individual. This openness is crucial for identifying true root causes and preventing future incidents by fixing systemic issues.
According to the U.S. Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality (AHRQ) Patient Safety Surveys, a database report indicated that 47 percent of respondents said that it feels like unsafe event reports are held against them.
Consequently, it’s imperative for leadership to foster a culture of safety where the imperative of addressing safety concerns supersedes the apprehension of punitive consequences.
2. Engage in Effective Questioning
Asking the right questions is key to uncovering the root cause. Use techniques like the “5 Whys” method, where the question “why” is asked continuously until the underlying cause is identified. This iterative questioning can reveal surprising insights and lead to an effective root cause analysis. For example, consider the problem that patient falls have increased in the last quarter:

The root cause in this particular 5 Whys scenario is the patient’s walker was moved by housekeeping and was not immediately accessible to the patient.
3. Gather Comprehensive Patient and Operational Data
Collect detailed information about the incident, including patient records, staff reports, and operational data. Healthcare is complex, and understanding the nuances of each case is crucial for an accurate analysis. Ensure data privacy and confidentiality are maintained throughout the process.
The quality of your analysis is directly tied to the data you gather. Therefore, it’s crucial to compile detailed, precise, and reliable information regarding the incidents for a thorough analysis.
4. Look Beyond the Immediate Clinical Incident
In healthcare, the root causes often extend beyond the immediate clinical scenario. Examine organizational processes, team dynamics, equipment, and environmental factors. Understanding the broader context can provide significant insights into underlying issues.
5. Involve a Multidisciplinary Team
Include a diverse team in your RCA process. This team should include clinicians, nurses, support staff, and even patients or their families where appropriate. Include individuals who have direct knowledge of the processes and systems involved, as well as those who can provide unique perspectives. Different perspectives can lead to a more comprehensive understanding of the incident.
6: Focus on High-Impact Areas
Prioritize issues that have the most significant impact on patient safety and care quality. Addressing these key areas can lead to substantial improvements in healthcare delivery. Concentrating on critical factors that can lead to significant improvements will make your healthcare root cause analysis efforts more valuable.
7: Utilize Specific Healthcare RCA Tools & Framework
Employ RCA tools and frameworks designed specifically for healthcare, such as the Fishbone Diagram or the Failure Mode and Effects Analysis (FMEA). A fishbone diagram helps team members visually diagram a problem or condition’s root causes, whereas FMEA is useful for identifying potential failures, gathering data for decision-making, and proactive risk control.
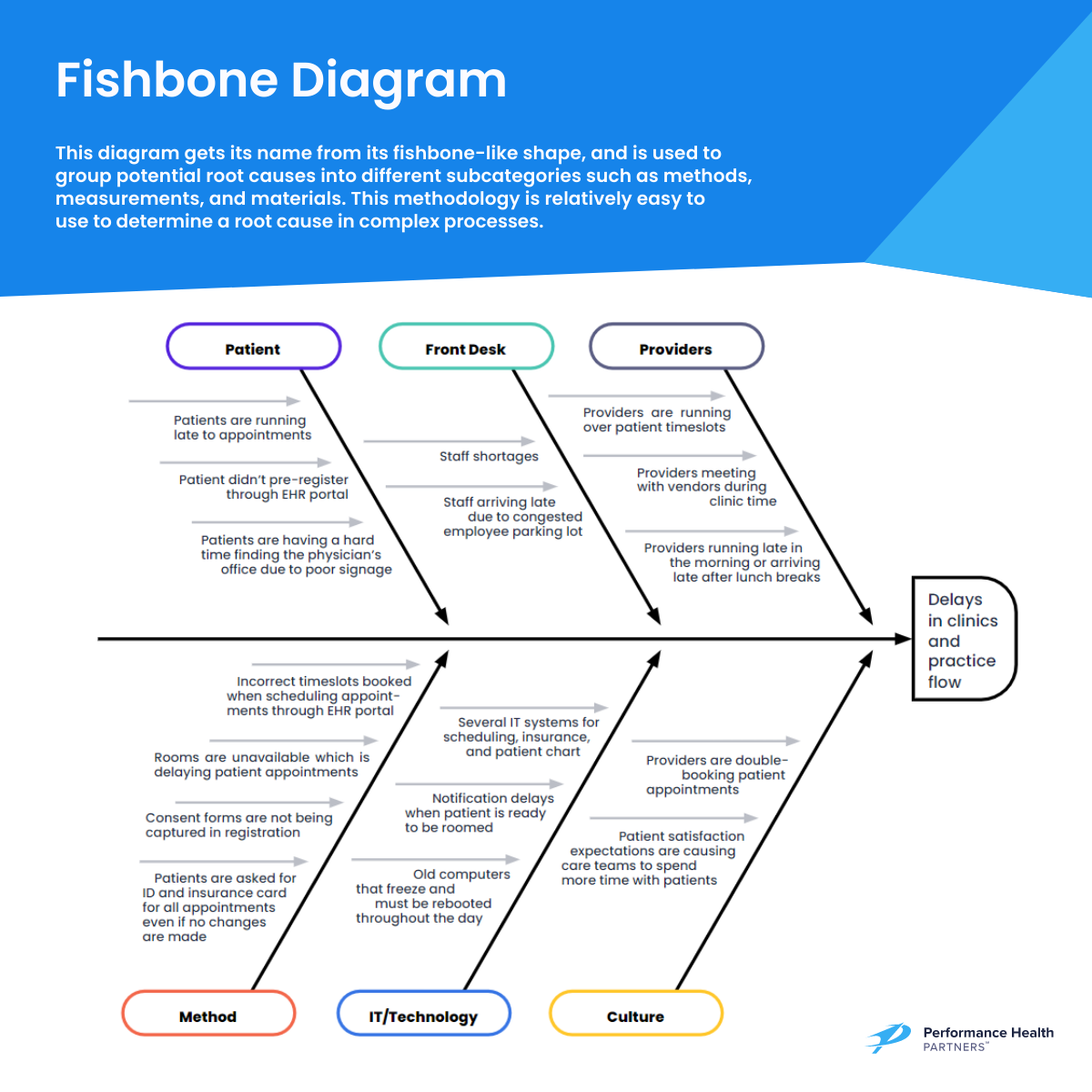
Imagine there is a significant increase in delays in clinics and practice flow. A fishbone diagram would be structured with the problem (delays) at the “head” of the fish, and various “bones” categorizing potential causes: patient, front desk, providers, method, technology, and culture.
In a healthcare setting, FMEA can aid in avoiding or reducing the gaps and errors that cause patient harm. These tools can help in structuring your analysis and ensuring that you consider all relevant healthcare-specific factors.
Other tools that can be used to perform an effective root cause analysis, specifically for medical errors, include event story maps and cause and effect diagrams.
8: Incorporate Technology
Software can enhance the efficiency of the root cause analysis process by effortlessly consolidating claim, incident, and cause data into a unified platform. Tools specifically created for healthcare root cause analysis utilize a methodical approach to gather and scrutinize data, pinpoint and execute changes, and monitor the advancement of new strategies.
With these tools, you can select and apply the most suitable RCA model for the specific incident, obtaining precise, up-to-the-minute outcomes that swiftly pinpoint the root cause. This enables the prompt implementation of corrective actions to bolster safety.
Incident management software allows healthcare organizations to report issues quickly and predict patterns of process failures and underlying employee and patient safety issues. This can be beneficial when conducting a root cause analysis in healthcare.
9: Implement Changes and Monitor Outcomes
The final and crucial step is implementing the recommended changes discovered through the RCA process. This should be followed by a monitoring phase to assess the effectiveness of these changes in improving patient safety and care quality. Continue to assess success by monitoring trends over time, and making sure the prevalence of related events and incidents decreases.



