5 min read
Medication Errors: Why We Must Look Beyond the “Five Rights”
Performance Health Partners
September 22, 2023

Medication errors are a widespread concern in healthcare, and they can have severe consequences for patients. The five rights of medication administration – right patient, right drug, right dose, right rout, and right time –have long been used as a framework for preventing medication errors. However, relying solely on the five rights is not enough to prevent medication errors, and failure to look beyond them can lead to significant risks for patients.
Medication Errors, By the Numbers
According to the National Coordinating Council for Medication Error Reporting and Prevention, a medication error is any preventable event that may cause or lead to an inappropriate medication use or patient harm while the medication is in the control of healthcare professionals, patients, or consumers. Medication errors occur throughout the medication-use system, including during prescription, computer input, preparation, and administration.
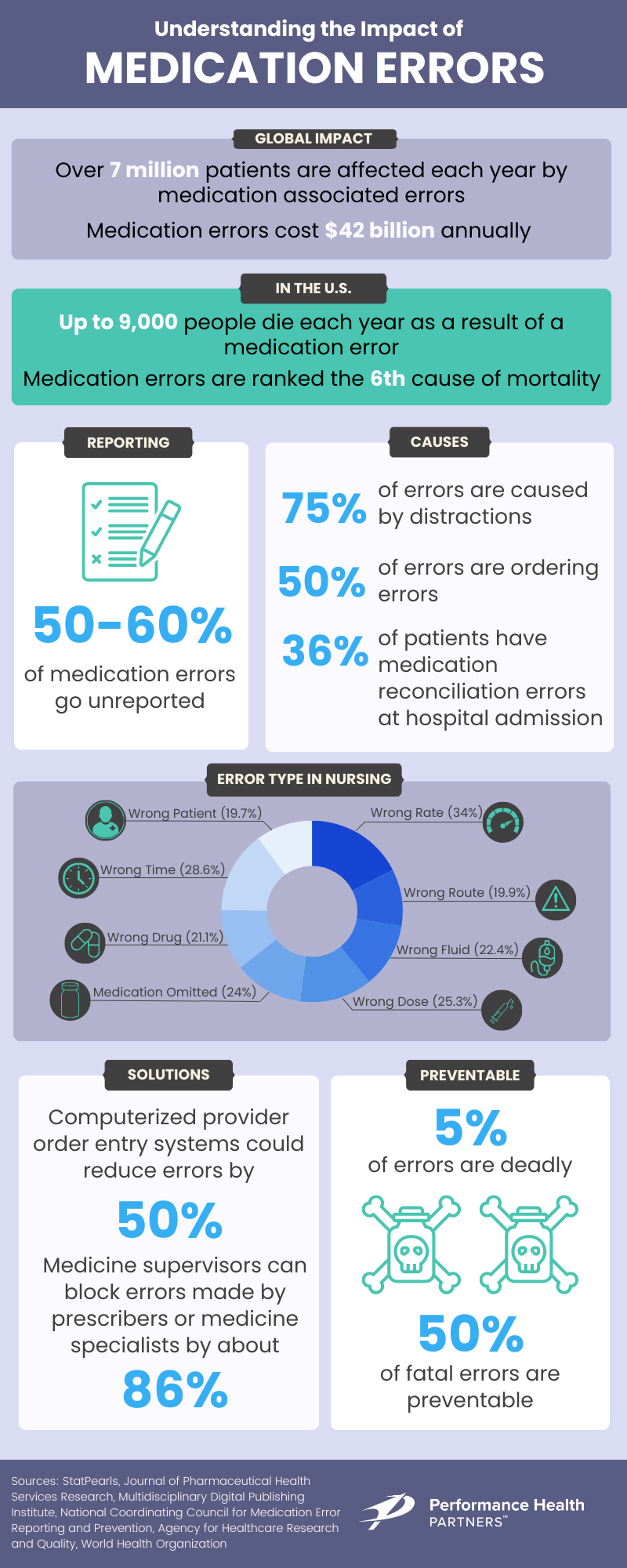
Harmful effects of medication errors may include death, life-threatening situations, hospitalization, disability, and birth defects. Up to 91% of medication reconciliation errors are clinically significant, and up to 2% are serious or potentially life-threatening.
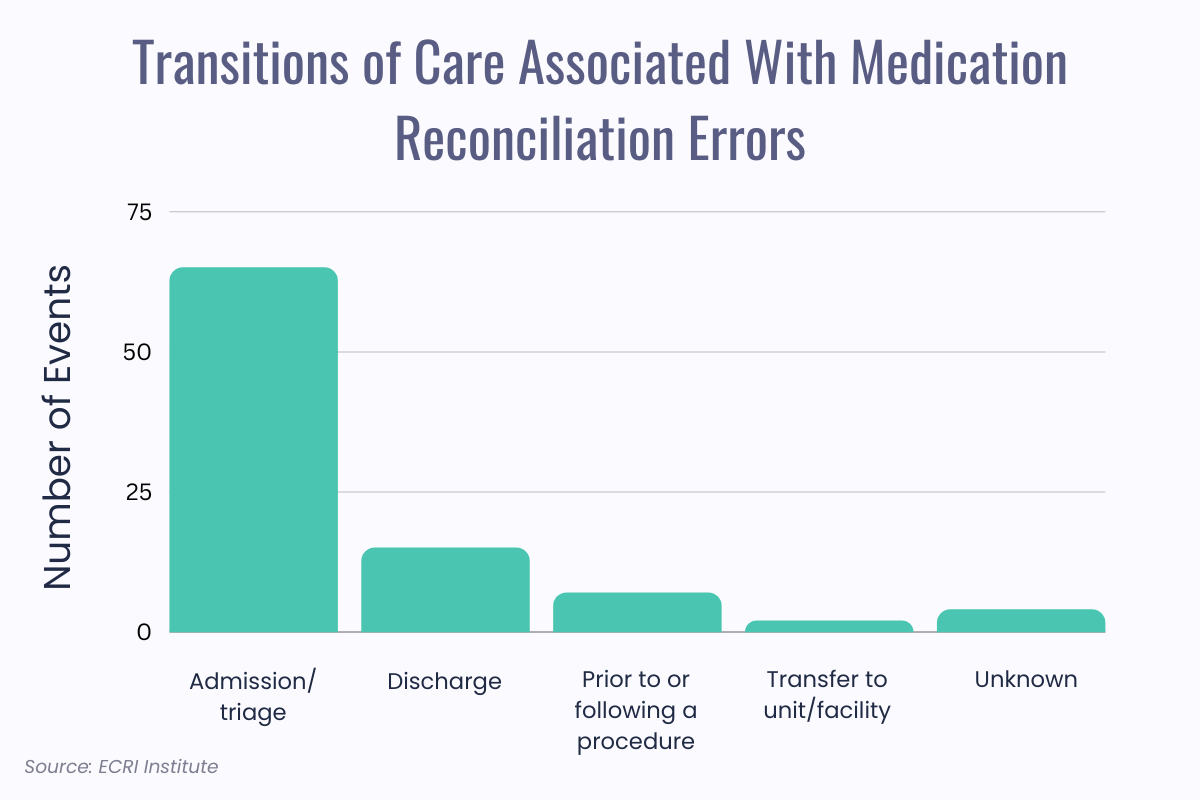
Inconsistent knowledge and record keeping about medications causes up to 50% of medication errors in hospitals and up to 20% of adverse drug events. Medication reconciliation errors at hospital admission are noted in 36% of patients and occur mostly during the medication history-gathering phase, as this phase often includes medications that the patient was no longer taking or because a medication was omitted.
Medication errors affect patient safety in two main ways: increasing mortality and morbidity rates as well as carrying an economic burden. In the United States alone, 7,000-9,000 people die each year as a result of a medication error. Besides death, patients with medical errors can also suffer psychological and physical pain.
With the large number of substances on the market, it is possible that practitioners make a mistake when prescribing or dispensing a drug. There is also a high risk of interaction between substances. The yearly total cost of looking after patients with medication-associated errors exceeds $40 billion. Besides costing hospitals money, errors also lead to decreased patient satisfaction and a lack of trust in the healthcare system.
Causes of medication errors include:
- Expired product
- Incorrect duration
- Incorrect preparation
- Incorrect strength
- Incorrect rate
- Incorrect timing
- Incorrect dose
- Incorrect patient action
- Unknown allergen
- Distractions
- Illegible writing
- Use of abbreviations
What Are The Five Rights of Medication Administration?
The five rights are a commonly used framework to ensure safe medication administration. The five rights are:
- Patient: Ensure that the medication is intended for the correct patient.
- Drug: Ensure that the medication being administered is the correct drug and formulation that was ordered by the healthcare provider.
- Dose: Ensure that the patient receives the appropriate amount of medication.
- Route: Ensure that the medication is given by the correct route.
- Time: Administer the medication at the right time.
Looking Beyond the Five Rights to Prevent Medication Errors
It is important to look beyond solely the implementation of the five rights of medication administration, as this framework is not enough to prevent all medication errors. While the five rights provide a foundation for medication safety, they are not foolproof and errors can still occur. Risks of not looking beyond the five rights can include:
- Communication breakdowns: Communication breakdowns are a common cause of medication errors, and can occur between healthcare providers, between healthcare providers and patients, or between different departments within a healthcare organization. Only using the five rights can result in a failure to address communication issues that can lead to medication errors.
- System failures: Medication errors can also occur due to system failures, such as inadequate medication storage, incorrect labeling of medications, or a lack of standardized medication administration procedures. Not looking beyond the five rights can result in a failure to identify and address these system failures.
- Lack of knowledge and training: Medication errors can occur due to a lack of knowledge or training among healthcare providers. Only implementing the five rights as a prevention effort can result in a failure to address knowledge and training gaps that can lead to medication errors.
- Medication interactions: Not looking beyond the five rights can result in a failure to identify and address potential medication interactions that can lead to adverse drug events.
- Patient harm: Ultimately, failure to look beyond the five rights can lead to patient harm. Medication errors can cause adverse drug events, delays in treatment, or even death. Patients may experience physical harm or psychological harm because of medication errors, and the emotional and financial costs can be significant.
Action Recommendations to Reduce Medication Errors
In addition to implementing the five rights of medication administration, healthcare providers can take additional steps to prevent medication errors and improve patient safety. Below are some action recommendations for healthcare providers to reduce the amount of medication errors at their practice:
Culture, Leadership, and Governance
To improve care coordination, it is essential to prioritize improvement initiatives that address health inequities and involve mobilizing stakeholders, assigning responsibilities, and allocating necessary resources. Clinical councils can help develop key performance indicators, and leadership should establish multidisciplinary care coordination teams that involve a variety of healthcare workforce members. To foster a culture of safety, healthcare providers should be encouraged to work as a team and communicate effectively. Additionally, providers should be encouraged to speak up if they notice any potential medication errors, to prevent harm to patients.
Patient and Family Engagement
To prioritize patient and family education, healthcare facilities should focus on various aspects of care. First, increasing shared decision-making and advance care planning is crucial. This can be achieved through patient and family education, which should emphasize the importance of involving patients and their families in the decision-making process. Additionally, discharge planning and post-discharge follow-up should be prioritized to ensure patients are prepared for their transition out of the hospital and have the necessary resources to continue their care at home.
To improve culturally and linguistically competent care, healthcare facilities should provide translated patient materials and consider engagement activities that involve patients and their families in different areas of the hospital. By creating a welcoming and inclusive environment, patients and families are more likely to be engaged in their care.
Furthermore, educating patients about their medications is critical to medication safety. Patients should be informed about the purpose, dosage, and potential side effects of their medications, and encouraged to ask questions and be active participants in their medication care. This can be achieved through patient education materials and direct communication with healthcare providers.

Workforce Safety
Promote collaboration to build mutual trust among healthcare providers, which can improve patient outcomes. Ensure safe staffing levels and provide proactive mental health support to prevent burnout and enhance staff well-being.
Equip staff with the necessary resources and training to effectively address frustrated patients and their families, including de-escalation techniques and backup safety mechanisms. Conduct regular medication safety audits and evaluations to identify areas for improvement, and implement changes as needed to enhance patient safety and reduce medication errors.
Learning System
To improve patient safety, it is important to address competency gaps in interprofessional and patient communication. It is also crucial to consistently conduct causal analyses of coordination- and communication-related adverse events to identify areas for improvement and make necessary changes quickly. Technology, such as electronic health records, barcode scanning, and computerized physician order entry systems, can reduce the risk of medication errors.
Implementing a double-check process, where a second nurse performs a completely independent evaluation prior to medication administration, is another effective method for preventing errors. Research shows that a true independent double-check process can detect up to 93% of errors.
By implementing these action recommendations, healthcare providers can ensure that they are providing safe and effective medication care to their patients.
Medication Error Prevention for Healthcare Providers
To ensure patient safety and prevent medication errors, it is crucial for healthcare organizations to take all necessary precautions. Performance Health Partners offers an incident reporting system that enables organizations to gather essential data, identify areas of fragmentation within their care delivery systems, and implement effective solutions to improve patient safety.
Learn more how your healthcare organization can utilize our system to prevent medication errors and improve the overall quality of care for their patients. Book a demo with our team today.


