4 min read
Enterprise Risk Management in Healthcare: A Collaborative Approach
Performance Health Partners
August 14, 2024

Healthcare risk management technology is very effective in supporting risk avoidance when used to support well-designed care processes. Read on to find out how incorporating it into your organization's risk management strategy can improve patient safety and outcomes.
What is Risk Management?
The Department of Health and Human Services states the risk management definition as: "any activity, process, or policy to reduce liability exposure” with an emphasis on “preventing harm to patients and reducing medical malpractice claims.”
In the most recent annual report, the Health Resources and Services Administration demonstrated that the number of medical malpractice practice reports has been trending downward since 1991 but the average payment amount for medical malpractice has trended upward during that same time period (see Graphs 1 and 2 below). 2
In other words, safety efforts to reduce harm to patients have resulted in fewer medical malpractice claims filed, but the payments have increased for those medical malpractice claims that were filed over the same time period.
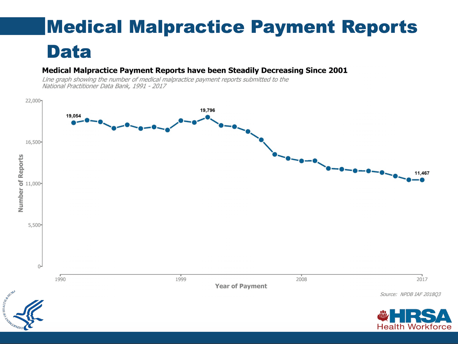
Graph 1- Source: https://www.npdb.hrsa.gov/community_n_education/2019presentations/MedicalMalpracticePaymentReportsEdForum.pdf
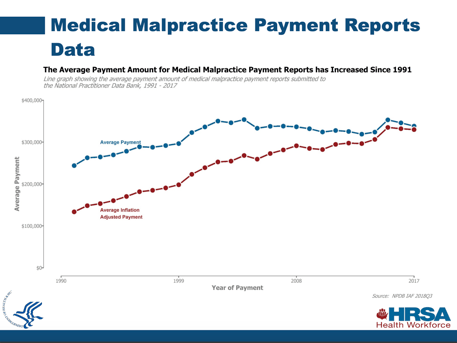
Graph 2- Source: https://www.npdb.hrsa.gov/community_n_education/2019presentations/MedicalMalpracticePaymentReportsEdForum.pdf
What is Enterprise Risk Management (ERM) in Healthcare?
While risk managers lead proactive efforts to promote zero harm in their organizations, the most effective outcomes occur when risk prevention, reporting, remediation, and learning is an organizational initiative – not just one department or team.
In 2014, the American Society for Healthcare Risk Management published a white paper on Enterprise Risk Management (ERM) that “promotes a comprehensive framework for making risk management decisions which maximizes value protection and creation by managing risk and uncertainty and their connections to total value.” 3
The elements of enterprise risk management in healthcare include:
- Comprehensive framework - including an organization-wide approach to risk management. This is a collaborative approach amongst disciplines including leaders in patient safety, quality, compliance, clinical teams, and executive team.
- Value protection - including focus on quality outcomes, patient safety, and efficient use of resources.
- Value creation - including strategies to increase market share, improve return on investment (ROI), and improve patient satisfaction.
- Managing uncertainty - reduce risks, promote standardization and reduce variability. 3
Safety Just Culture is Key
A Safety Just Culture, also known as a non-punitive environment, is one of the best ways to ensure all team members feel comfortable in reporting incidents, reporting near-misses or good catches, identifying potential risks for an event, and participating in risk management activities. 7
Providing a safe, open space for every member of a healthcare team to address risk is the first step in establishing a culture of risk management.
An organization should also put processes in place to make incident reporting easy for staff. An enterprise risk management software can simplify incident reporting and provide a tracking mechanism to show progress towards identifying root causes. Dashboards and analytics make it easy to identify trends and resources needed to improve patient safety. The incident reporting system should also be robust enough to indicate steps to reduce the risk of reoccurrence of a similar event in the future.
When all team members collaborate and recognize risk management as their responsibility, there is notable improvement in quality of care and patient safety. 9
Risk Prevention and Remediation
Stable processes and systems that are reproducible are required to minimize organizational risks. A process must first be stabilized then standardized before being effective.
Healthcare risk management technology is very effective in supporting risk avoidance when used to support well-designed care processes. The elements of risk management in patient safety include:
-
Preventing incidents: The first step in preventing incidents is to identify risks in health care services and the health care environment. From there, the level of risk is analyzed and underlying causes of the risk are identified. Interventions to reduce risk are put in place to prevent incidents; examples include checklists, rounding, trainings, policies & procedures, and alarms. 6
For example, Mills et al reported on interventions taken by the Veterans Affairs system for decreasing adverse drug events (ADEs). After compiling data from 143 Root Cause Analyses (RCAs) involving ADEs, they implemented an intervention to change the process of medication order entry by using alerts or forcing functions in the electronic health record. This intervention was positively correlated with improved outcomes and less ADEs across the system. 9 - Incident reporting: Everyone makes mistakes, even doctors and nurses. Incident reporting should be easy and accessible to all team members. By promoting a Just Culture, employees feel more empowered to participate in the Patient Safety process and learn from process flaws. 5
-
Post-event follow-up: Create a central repository for team communications, follow-up actions, and next steps. Recently, some organizations have adopted the Communication and Optimal Resolution process to respond to patients and families “in a timely, thorough, and just way when unexpected events cause patient harm.” 8 CANDOR provides structure in communicating with patients and families after a harmful incident has occurred.
-
Root Cause Analysis (RCA): A systematic approach is utilized to identify the underlying causes of adverse event in order to take effective steps to modify processes and prevent future incidents. 6
Why is Enterprise Risk Management in Healthcare Important?
Risk management strategies are designed to prevent and mitigate financial losses. In healthcare, there is the added importance of patient safety and preventing harm. Risk management in healthcare is designed to reduce non-injury events and injury events that might literally mean life or death to patients. 4
Interested in learning more about risk management in healthcare? Connect with our team.
Trudi Stafford, PinhD, RN, and Clinical Advisor at PHP shares insight on a collaborative approach to risk management amongst patient safety, quality, compliance, clinical, and executive teams.
Trudi Stafford has 30+ years of health care leadership experience with an emphasis on informatics to positively impact patient safety and health care quality. She is a doctorally prepared nurse executive with prior work experience as the Chief Nursing Office at three of the nation’s largest health systems.
References
-
OIG Final Report: Risk Management at Health Centers (OEI-01-03-00050). (Feb 17, 2005). Retrieved on 8/13/2019 at https://oig.hhs.gov/oei/reports/oei-01-03-00050.pdf
-
Wiley, M & Lotterer, P. (April 2019). National Practitioner Data Bank: Partnering to Protect Patients Medical Malpractice Payment Reports. Health Resources and Services Administration. Retrieved on August 13, 2019 at https://www.npdb.hrsa.gov/community_n_education/2019presentations/MedicalMalpracticePaymentReportsEdForum.pdf
-
Carroll, RL. (2014). Enterprise Risk Management: A Framework For Success. American Society for Healthcare Risk Management. Retrieved on August 13, 2019 at https://www.ashrm.org/sites/default/files/ashrm/ERM-White-Paper-8-29-14-FINAL.pdf
-
Mosowitz, D. (March 28,2018). The Importance of Healthcare Risk Management. Investopedia. Retrieved on August 13, 2019 at https://www.investopedia.com/articles/personal-finance/072315/importance-healthcare-risk-management.asp
-
Fetherston, T. (2015). The importance of critical incident reporting — and how to do it. Community Eye Health.28(90): 26–27. Retrieved on August 13, 2019 at https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4675258/
-
Alam, AY. (October 3, 2016) Steps in the Process of Risk Management in Healthcare. Epidemiology and Preventive Medicine. Retrieved on August 13, 2019 at https://www.elynsgroup.com/journal/article/steps-in-the-process-of-risk-management-in-healthcare
-
4 Best Practices for Hospital Risk Management. (April 1, 2013). Becker’s Clinical Leadership and Infection Control. Retrieved on August 19, 2019
at https://www.beckershospitalreview.com/quality/4-best-practices-for-hospital-risk-management.html
-
Communication and Optimal Resolution (CANDOR) Toolkit. Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality. Retrieved on August 16, 2019 at https://www.ahrq.gov/professionals/quality-patient-safety/patient-safety-resources/resources/candor/introduction.html
-
Mills PD, Neily J, Kinney LM, Bagian J, and Weeks WB. (2008) Effective interventions and implementation strategies to reduce adverse drug events in the Veterans Affairs (VA) system. Health Care. 17:37-46.



