2 min read
Navigating Rising Hospital Acquired Infections: Prevention Strategies
Performance Health Partners
September 25, 2023

In recent times, the healthcare industry has witnessed a concerning trend: a noticeable increase in hospital acquired infections (HAIs). This rise has underscored the urgent need for healthcare facilities to enhance their infection prevention strategies. In this blog post, we will delve into the reasons behind this surge in HAIs, explore effective infection prevention strategies, and emphasize the critical role that everyone, from healthcare professionals to patients, plays in curbing this concerning trend.
Understanding the Surge in HAIs
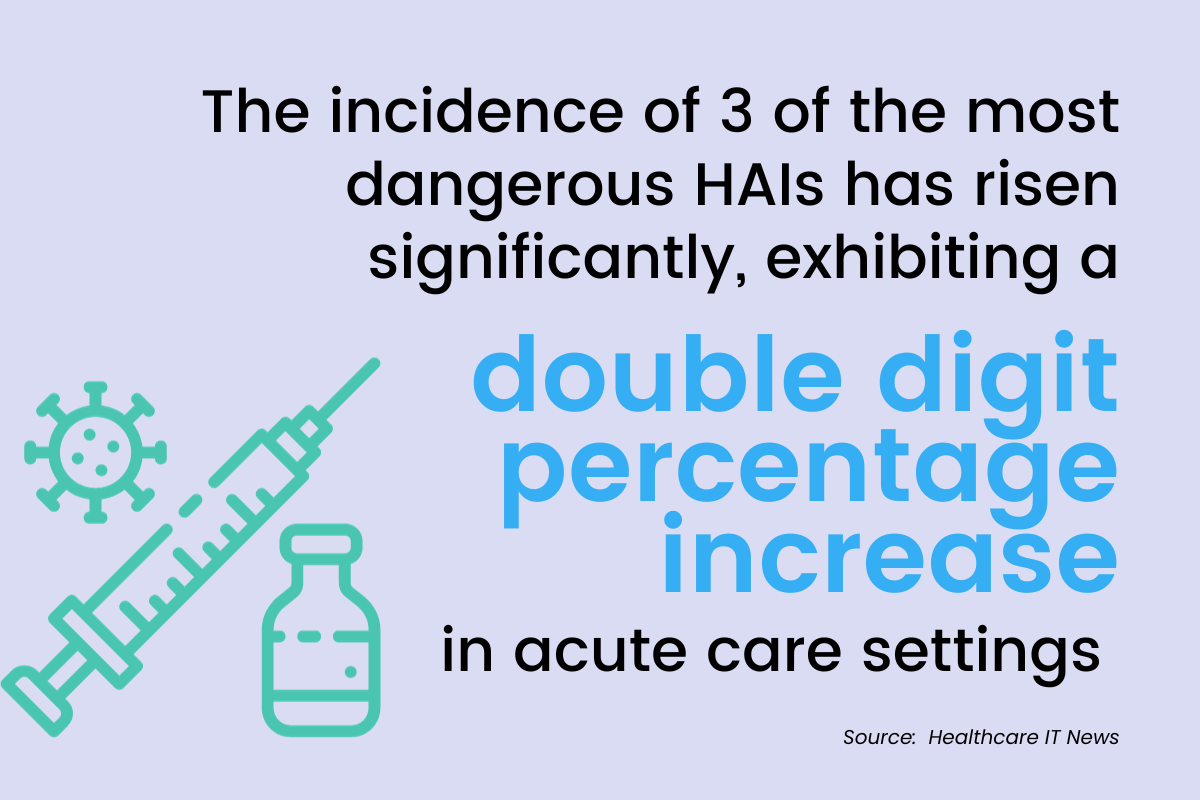
According to data from the new Leapfrog Report, three of the most dangerous HAIs have shown double-digit increases in acute care settings across the country. Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA), central line-associated bloodstream infections (CLABSI), and catheter-associated urinary tract infections (CAUTI) have all drastically increased, putting some patients in life-or-death positions.
CLABSI ratios increased most drastically, with data reporting a 60% increase from pre-pandemic to 2021 and 2022. Along with being an increasing cause of death, this rise in HAIs also increases length of hospital stay and costs.
Several factors have contributed to the recent rise in hospital acquired infections. These include the emergence of antibiotic-resistant strains of bacteria, increased patient acuity, and challenges posed by the global pandemic.
Last winter, nearly 80% of hospital beds across the United States were occupied. The pressure to manage a higher number of patients combined with limited resources and overwhelmed healthcare systems has created an environment where infections can easily spread.
Key Infection Prevention Strategies
Addressing the surge in HAIs requires a multifaceted approach that tackles both immediate concerns and long-term prevention. Healthcare organizations must invest time and effort into infection prevention control and promoting patient safety. Here are seven essential strategies that healthcare facilities can implement to strengthen infection prevention:
- Hand Hygiene: Proper hand hygiene among healthcare workers remains paramount. Regular handwashing with soap and water or using alcohol-based hand sanitizers significantly reduces the risk of transmitting infections.
- Personal Protective Equipment (PPE): Healthcare professionals should consistently use appropriate PPE when interacting with patients. Gloves, masks, gowns, and eye protection serve as crucial barriers against infection transmission.
- Regular Cleaning: Thorough and regular cleaning of surfaces, equipment, and patient rooms helps eliminate potential sources of infection. Disinfection protocols should be strictly followed to ensure a safe environment.
- Antibiotic Stewardship: Preventing the development of antibiotic-resistant strains requires judicious use of antibiotics. Healthcare professionals should only prescribe antibiotics when necessary and ensure proper dosing and duration.
- Patient Screening and Isolation: Implementing screening protocols upon admission can identify patients carrying infections, enabling timely isolation and preventing the spread to others. Katelyn Jetelina, an epidemiologist at the University of Texas, states, “I think one of the most important things is, yes, filtration and ventilation, but stay home if you're sick." Isolating from others, whether you have the flu, cold, or COVID-19, proves to reduce the spread of infection and reduces hospitalizations.
- Education and Training: Continuous education of healthcare staff on infection prevention protocols is essential. Regular training sessions can reinforce proper practices and keep everyone informed about the latest guidelines.
- Communication: Transparent communication between healthcare teams, patients, and their families fosters a collaborative effort to prevent infections. Patients should feel empowered to advocate for their safety.
The Role of Incident Reporting Software on Infection Prevention
Hospital-acquired infections (HAIs) and incident reporting software are closely related in the context of healthcare facilities' overall safety and quality management. Incident reporting software plays a significant role in the prevention and management of HAIs by providing a systematic approach to identifying, reporting, investigating, and mitigating various types of incidents, including those related to infections such as sepsis.
Several ways that incident reporting technology can aid in infection control are listed below:
- Early detection and reporting of infections
- Rapid response and investigation
- Trend analysis and prevention strategies
- Continuous improvement
In navigating the complexities of infection prevention and the rise in HAIs, collaboration between healthcare professionals, patients, and families is essential. By collectively embracing these strategies and leveraging technology, we can work towards a future where hospital-acquired infections are minimized, patient safety and quality are paramount, and healthcare environments are safer for all.


